In 2015, countries agreed the Addis Ababa Action Agenda, which highlighted the need for integrated national financing frameworks to support nationally owned sustainable development plans. This report analyses, for the first time, the key steps required for establishing integrated national financing frameworks.
Ambitious agendas and diverse financing contexts
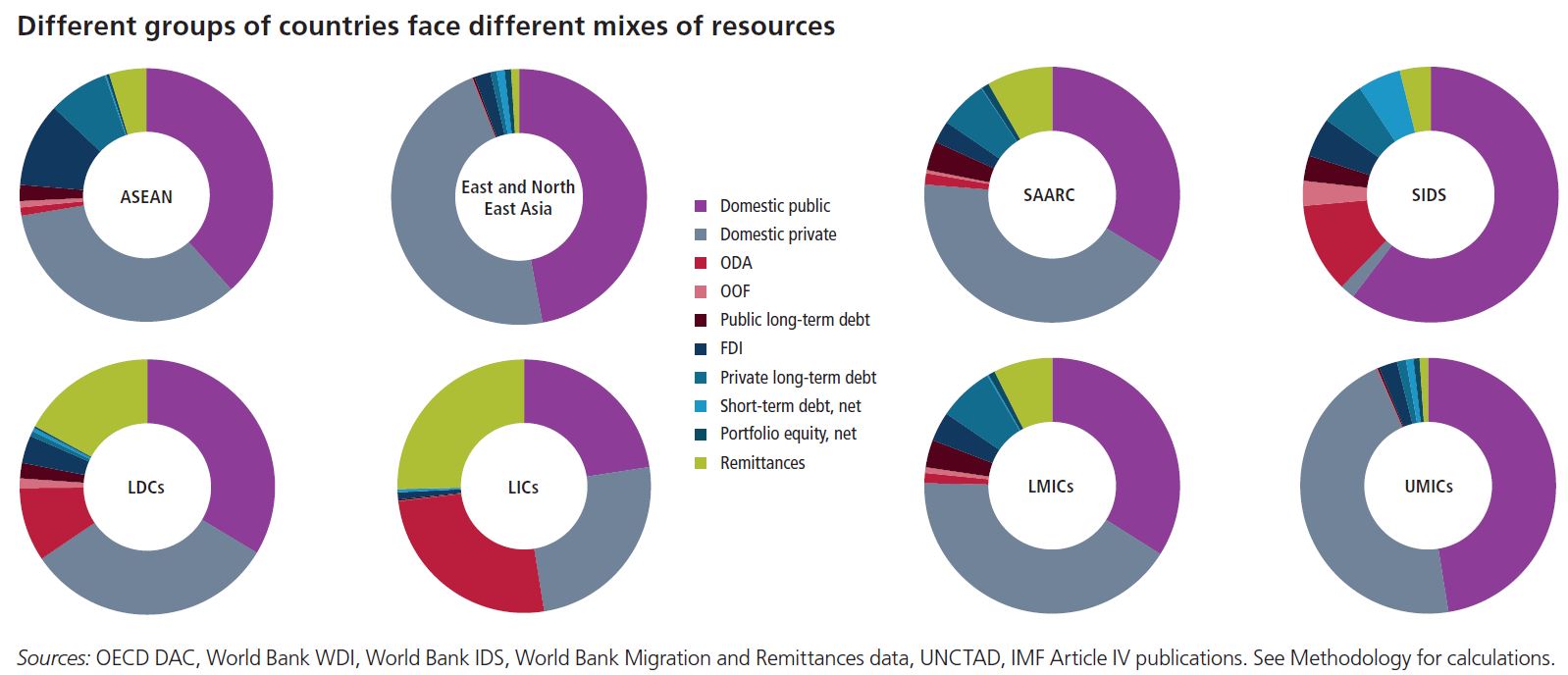
Countries across the Asia-Pacific region have high ambitions across a wide-ranging, interconnected sustainable development agenda. Realising this agenda will require mobilising and effective use of a diverse portfolio of public and private, domestic and international financing. For many countries in the region, financing flows have been growing rapidly, though the mix and levels vary widely across countries.
Integrated national financing frameworks
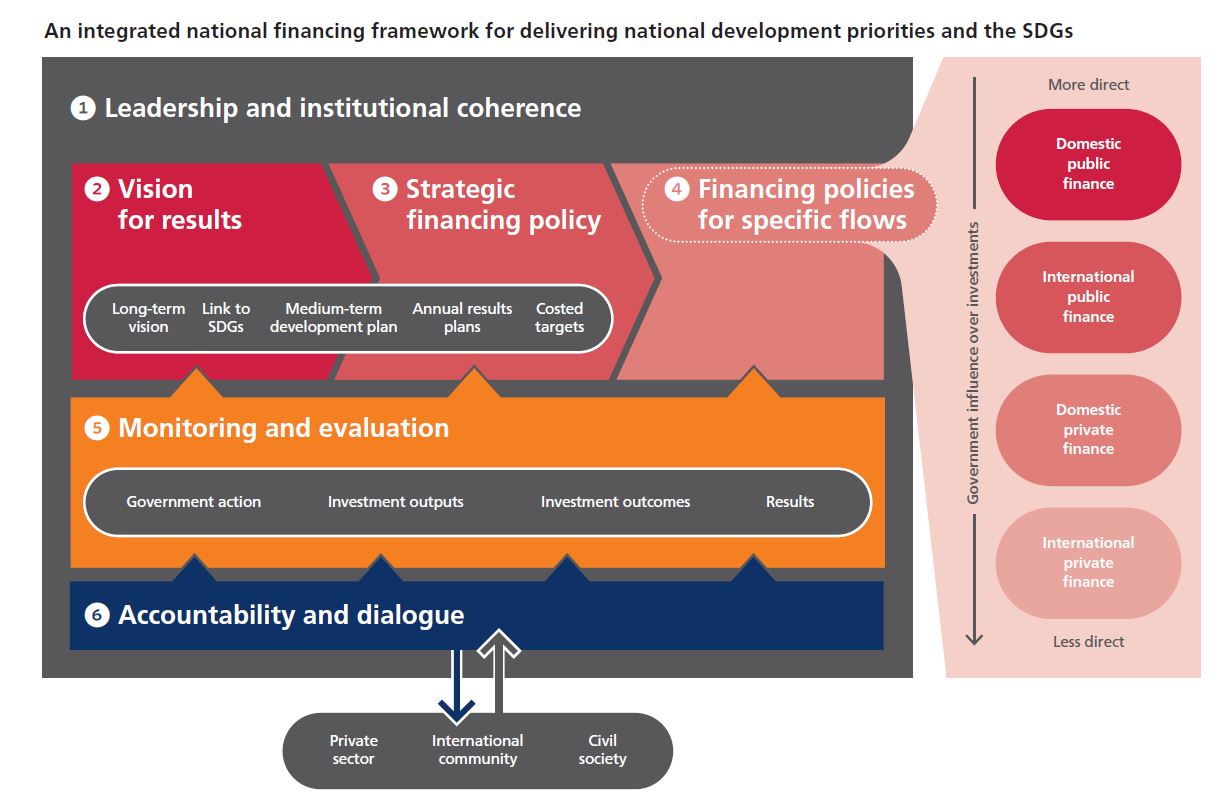
The report examines the strengths of the institutional structures, mechanisms and policies that governments across Asia and the Pacific have in place to mobilise and channel financing to realise sustainable development results. It draws from country-level evidence, including the Development Finance Assessments that countries in the region have undertaken. Six core features of financing frameworks that help develop long-term, holistic strategies to link financing with sustainable development results are identified. These six features can form the building blocks of the integrated national financing framework:
- Leadership that facilitates institutional coherence is essential for bringing together actors across and outside government to build an integrated approach and ensuring alignment in policies.
- A clear vision for results that the country wants to achieve is the foundation of an integrated national financing framework on which financing plans and targets are built.
- A strategic financing policy takes the long-term vision for results and develops estimates for the costs and types of investments needed. It provides a broad framework within which operational financing policies that mobilise the outputs leading to sustainable development impacts can be developed.
- Specific financing policies develop and deliver plans to mobilise each type of finance in a scale and manner consistent with the strategic financing policy. This covers a range of policies such as medium-term expenditure frameworks, tax revenue strategies, national aid policies and industrial development strategies.
- A strong monitoring, evaluation and learning system is an essential ingredient of results-focused planning and implementation.
- An enabling environment for accountability and dialogue is essential to build the trust necessary to mobilise contributions from stakeholders outside government; make sure policies are being designed and delivered effectively; and ensure a voice for citizens, civil society, business, development partners and other actors.
The beginning of the SDG era is an important moment for governments to assess their financing frameworks and consider how effectively they can shape and deliver financing policy for the future. The concept of an integrated national financing framework can help as a prompt to reflect on the strengths and weaknesses of existing financing frameworks as a whole, and a guide as governments undertake reforms. Indeed, a number of Asia-Pacific countries are already taking steps towards establishing an integrated national financing framework.
Download the report from the AP-DEF website here
About AP-DEF
This report was commissioned by AP-DEF through financial support from the Australian Government Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade and the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation.
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)’s Bangkok Regional Hub is the Secretariat for AP-DEF, a country-led regional platform, chaired by the Government of Bangladesh, which supports Asia-Pacific countries to implement their national agendas on development finance and cooperation.
Contact AP-DEF, UNDP Bangkok Regional Hub:
Thomas Beloe: [email protected]
Ashley Palmer: [email protected]
Emily Davis: [email protected]